Detail drawings are the cornerstone of precision in machine design and manufacturing. They provide a clear, comprehensive representation of each component, ensuring machinists can fabricate parts accurately without requiring additional instructions. By including fully dimensioned views, necessary annotations, and logical organization, these drawings bridge the gap between conceptual design and practical implementation.
Detail drawings are the cornerstone of precision in machine design and manufacturing. They provide a clear, comprehensive representation of each component, ensuring machinists can fabricate parts accurately without requiring additional instructions. By including fully dimensioned views, necessary annotations, and logical organization, these drawings bridge the gap between conceptual design and practical implementation.
What Are Detail Drawings?
A detail drawing focuses on individual parts of a machine, separating them from the complete assembly to highlight their specifications. These drawings are meticulously dimensioned and include enough views to ensure machinists understand the exact geometry, materials, and features of each piece. When necessary, notes accompany the visuals to further clarify construction methods or critical details.
Organizing Detail Drawings
The arrangement of detail drawings can follow various methodologies depending on manufacturing requirements:
- Logical Machine Order: Components are arranged in the sequence they appear within the machine. This approach simplifies visualization and aids in understanding the assembly’s structure.
- Functional Grouping: Details of parts intended for assembly in a specific area of the shop are grouped together. For example, parts for a gearbox assembly might be presented on the same sheet.
- Process-Based Grouping: Components requiring similar machining processes or produced by the same department are organized together. For instance:
- Shafts: Grouped to streamline production by the shaft-turning machinist.
- Gears: Presented collectively for gear-cutting specialists.
- Guards and Casings: Listed for those responsible for finishing and protective features.
The choice of grouping depends on manufacturing workflows, shop-floor efficiency, and assembly requirements.
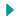
An Example: Crank End of a Connecting Rod
Let’s examine a practical example: the crank end of a connecting rod. This component, shown in the accompanying illustration, demonstrates how detail drawings convey intricate design features:
- Construction: The crank end utilizes a bolted strap design to handle the tension of the rod. The bolts’ shearing strength and the friction between the stub end and strap ensure a robust construction. This open-end design is particularly suited for center crank engines.
- Assembly Process:
- Place the boxes over the crank pin.
- Position the strap around the boxes.
- Secure the wedge using cap screws.
- Align the stub end between the jaws of the strap and fasten it with bolts.
This sequential approach simplifies assembly and ensures a secure, durable connection.
Material and Design Considerations
For components like the connecting rod crank end, material selection and design intricacies are critical:
- Box Construction:
- Made of cast iron with babbitted surfaces for friction resistance.
- Flanges prevent lateral movement, ensuring stability during operation.
- Babbitt Material:
- A fusible anti-friction metal that’s easy to apply and forms a perfect bearing surface.
- Eliminates the need for re-boring, reducing maintenance requirements.
- Wedge Mechanism:
- Adjusted using cap screws that pass through the strap and are tapped into the wedge.
- Ensures tight alignment and secure positioning of the boxes.
Why Detail Drawings Matter
Detail drawings go beyond simple illustrations; they’re a critical communication tool in manufacturing. By providing precise information and logical organization, these drawings:
- Minimize errors in fabrication.
- Enhance efficiency in assembly.
- Ensure consistency across production batches.
- Support innovation by translating complex ideas into actionable designs.
Conclusion
Whether you’re designing components for heavy-duty machinery or crafting intricate mechanical parts, detail drawings are indispensable. They embody the principles of clarity, precision, and practicality, ensuring machinists and engineers work seamlessly from concept to creation. By mastering the art of creating and interpreting these drawings, you’ll contribute to the reliability and success of every project you undertake.